Cellular Respiration Meaning In Biology

Cellular respiration refers to both aerobic and anaerobic respiration but is often synonymous with aerobic respiration.
Cellular respiration meaning in biology. Cellular respiration the process by which organisms combine oxygen with foodstuff molecules diverting the chemical energy in these substances into life-sustaining activities and discarding as waste products carbon dioxide and water. In this process glucose breaks down without the help of oxygen and the by-products produced are alcohol CO2 and energy or ATP. Cellular respiration is a biological process in which cells convert sugar amino acids and fatty acids into energy utilized by the cell.
In contrast to simple combustion cellular respiration involves the step-wise release of energy in a tightly regulated fashion. The principal carbohydrate formed through photosynthesis is glucose. Autotrophs like plants produce glucose during photosynthesis.
Cellular respiration can be described as the reverse or opposite of photosynthesis. In the cells of any non-photosynthetic eukaryote such as a person bread mold or a paramecium glucose and oxygen are going to come from outside the cell. The respiration occurring at the cellular level wherein the cells produce energy by combining oxygen with food molecules is called cellular respiration.
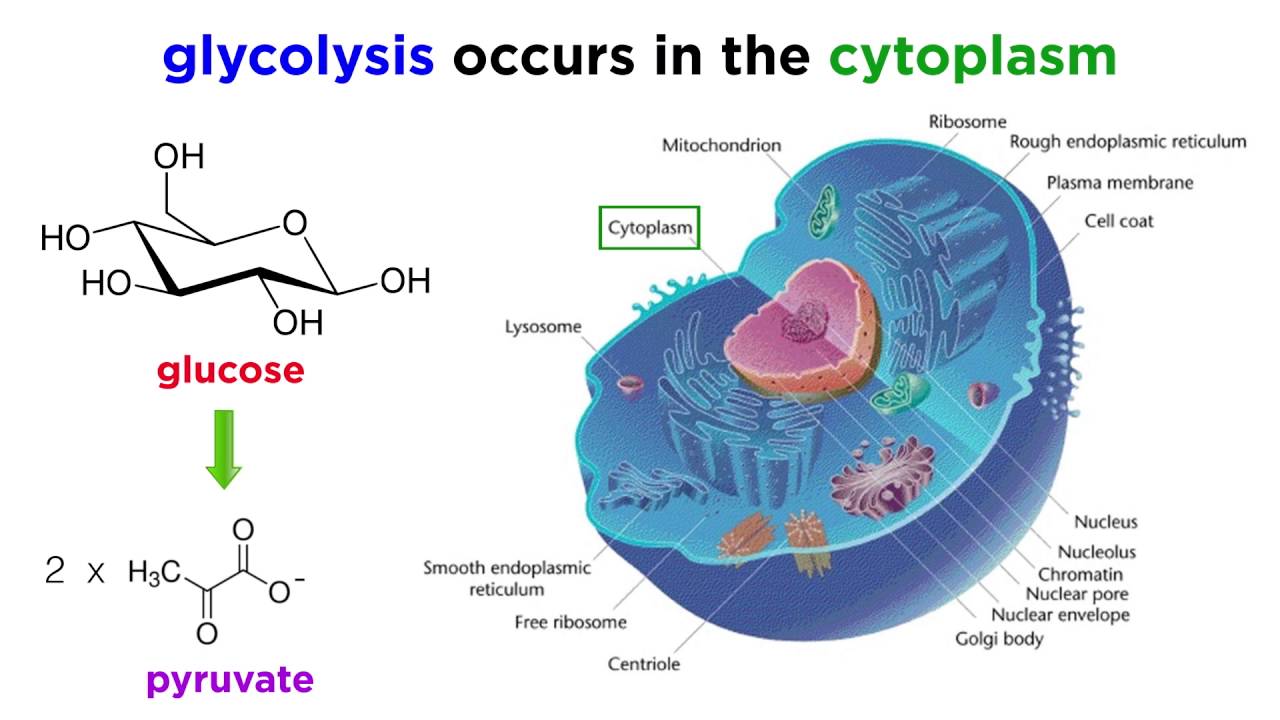
The process takes place in the cytoplasm of a cell. Cellular respiration is a process that all living things use to convert glucose into energy. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy from oxygen molecules or nutrients into adenosine triphosphate ATP and then release waste products.
Cellular respiration Cellular respiration n. Introduction to Cellular Respiration. Related Biology Terms.
Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions that take place in all living cells to release energy by converting biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate- ATP. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis pyruvate oxidation the citric acid or Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. Cellular respiration is the process through which cells convert sugars into energy.