Deep Ocean Animals Adaptations
Rods help eyes sense light.
Deep ocean animals adaptations. Coastal plants need special adaptations to survive. REVIEWS Are there physiological and biochemical adaptations of metabolism in deep-sea animals. Many shellfish like.
Deep Ocean Animal Adaptations These lessons are part of a deep ocean unit. They have streamlined bodies to help them swim fast and gills that suck the oxygen out of the water so they can breathe. 4000 m 6000 m and Hadal from 6000 m and below zones Pelagic division includes Mesopelagic 200.
In some other deep-sea fishes eyes are very small as they are of little apparent use and still others are without eyes. Some of the most amazing adaptations are from ocean animals like sharks jellies starfish stingrays and dolphins. Contains a chart for students to label the different zones of the ocean as well as a chart to keep track of different animalcreature adaptations in different zones.
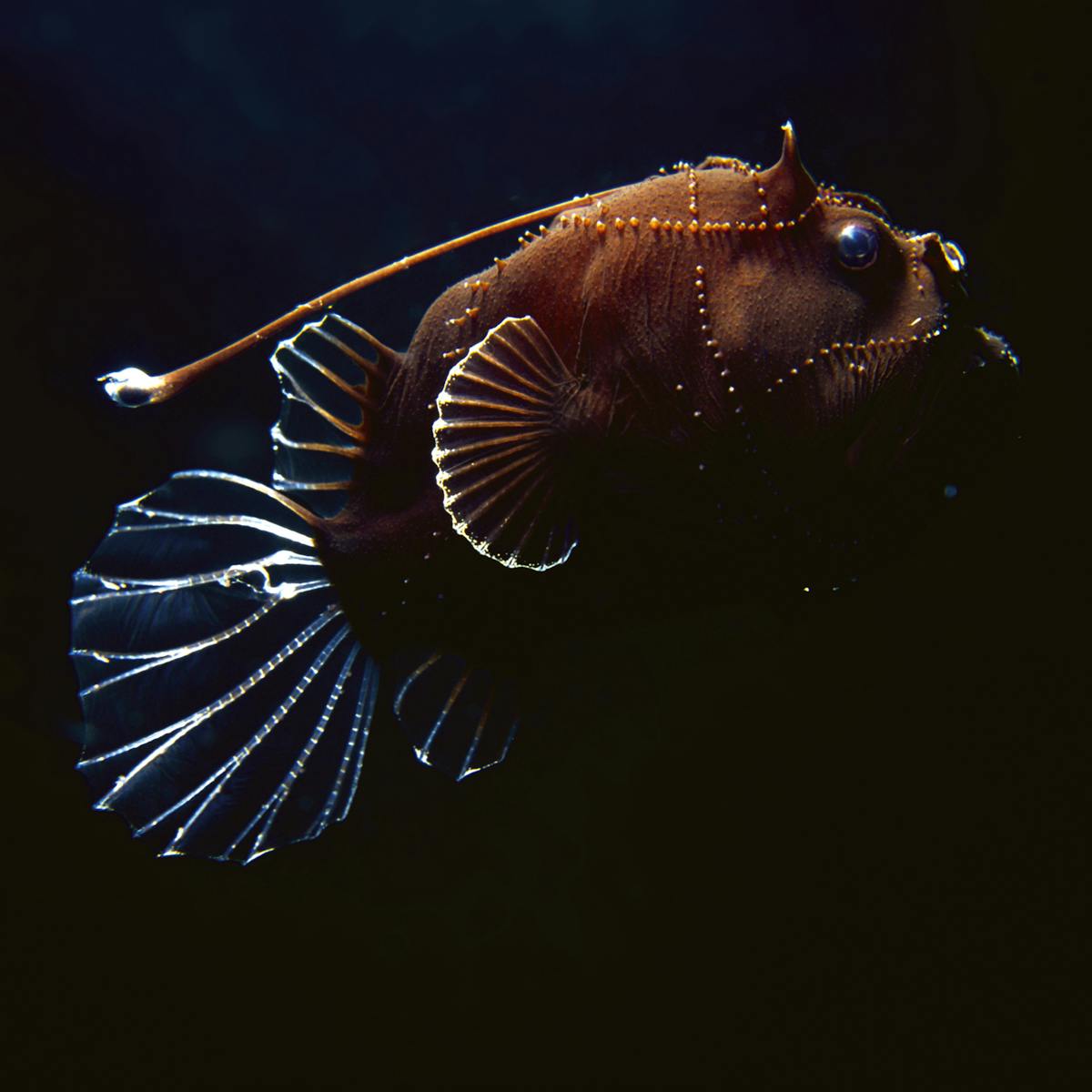
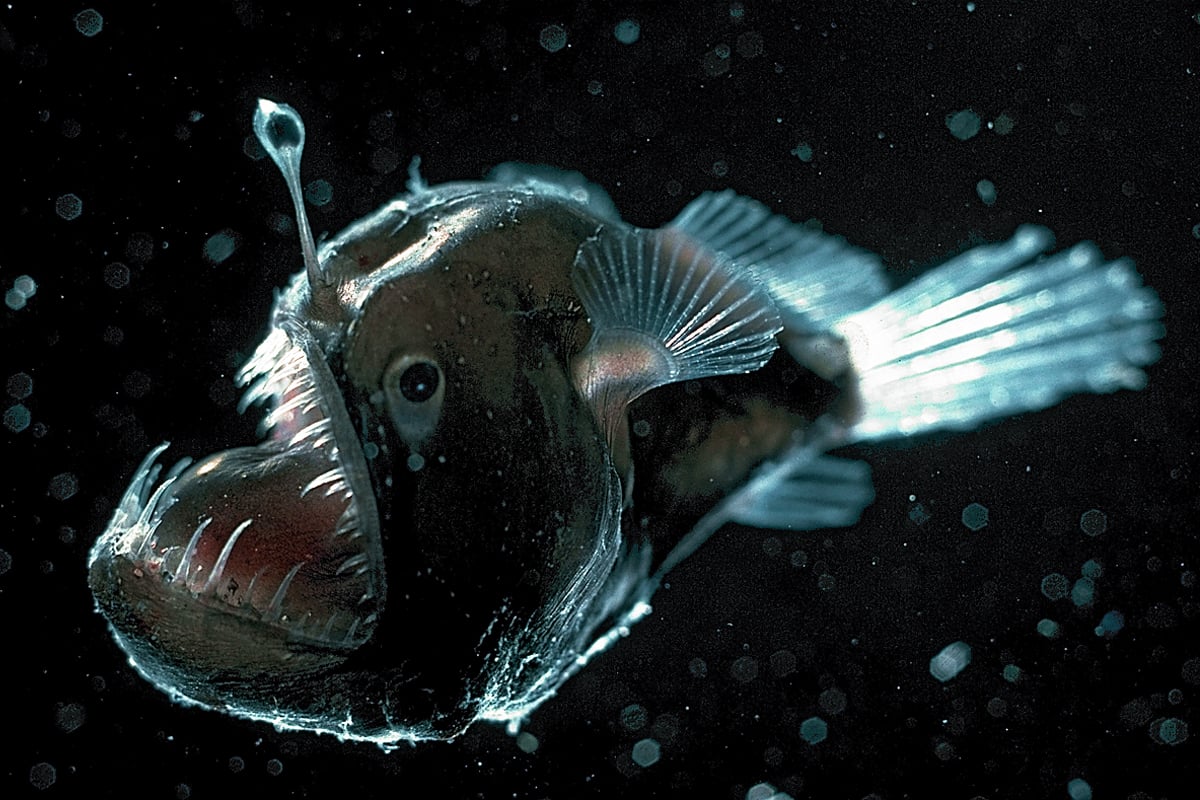
Many deep-sea animals produce their own light by means of luminous organs eg lantern fish. First off the deep ocean is dark because sunlight cant penetrate very far into the water. Enzymes exhibit reduced perturbation of function by pressure membranes have fluidities adapted to deep-sea pressures and temperatures and proteins show.
Deep sea creatures have evolved some fascinating feeding mechanisms because food is scarce in these zones. 8 12 x 11 blank paper pencil colored pencils ruler or straight edge. Dissolved H2S emerging from.
In the deep sea animals bodies are often transparent eg Squid and Jelly fishes. The intertidal zone the pelagic zone and the abyss. Ocean animals have unique adaptations depending on what ocean habitat they live in.


















