Food Chain Definition Biology

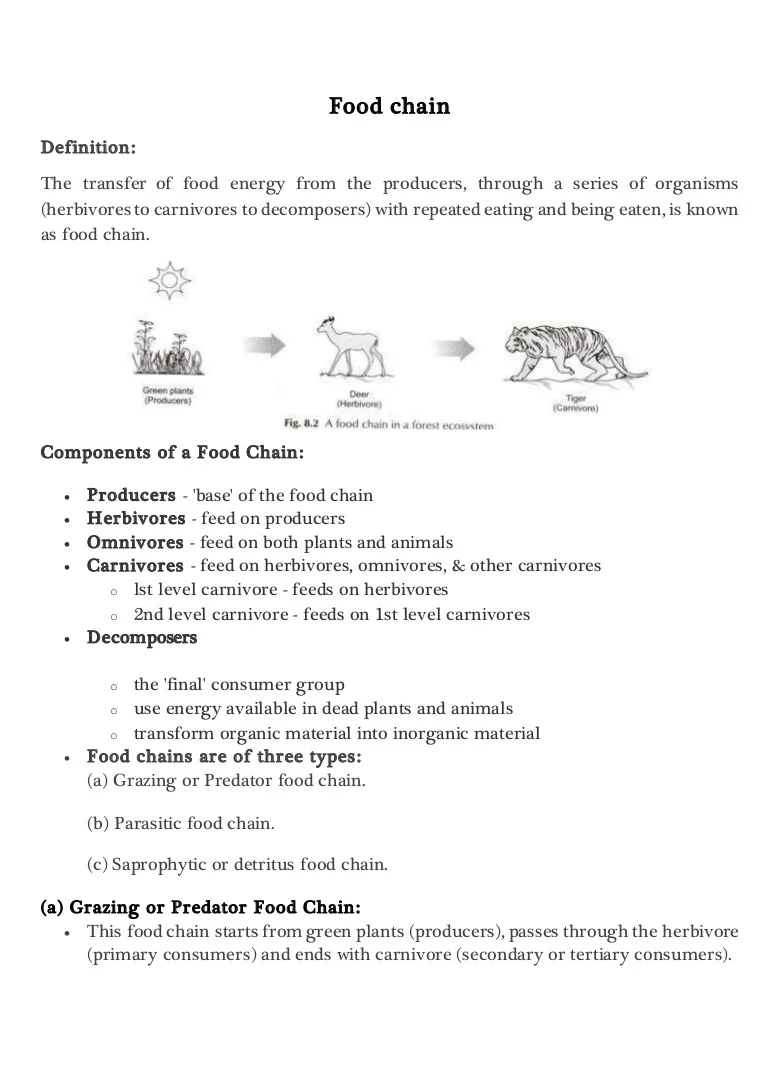
It begins with producer organism follows the chain and ends with decomposer organism.
Food chain definition biology. Food Chain Definition Biology Idalias Salon. The dead organic substances are decomposed by microorganisms. It is the process by which nutrients are transferred between the different species that make up a biological community.
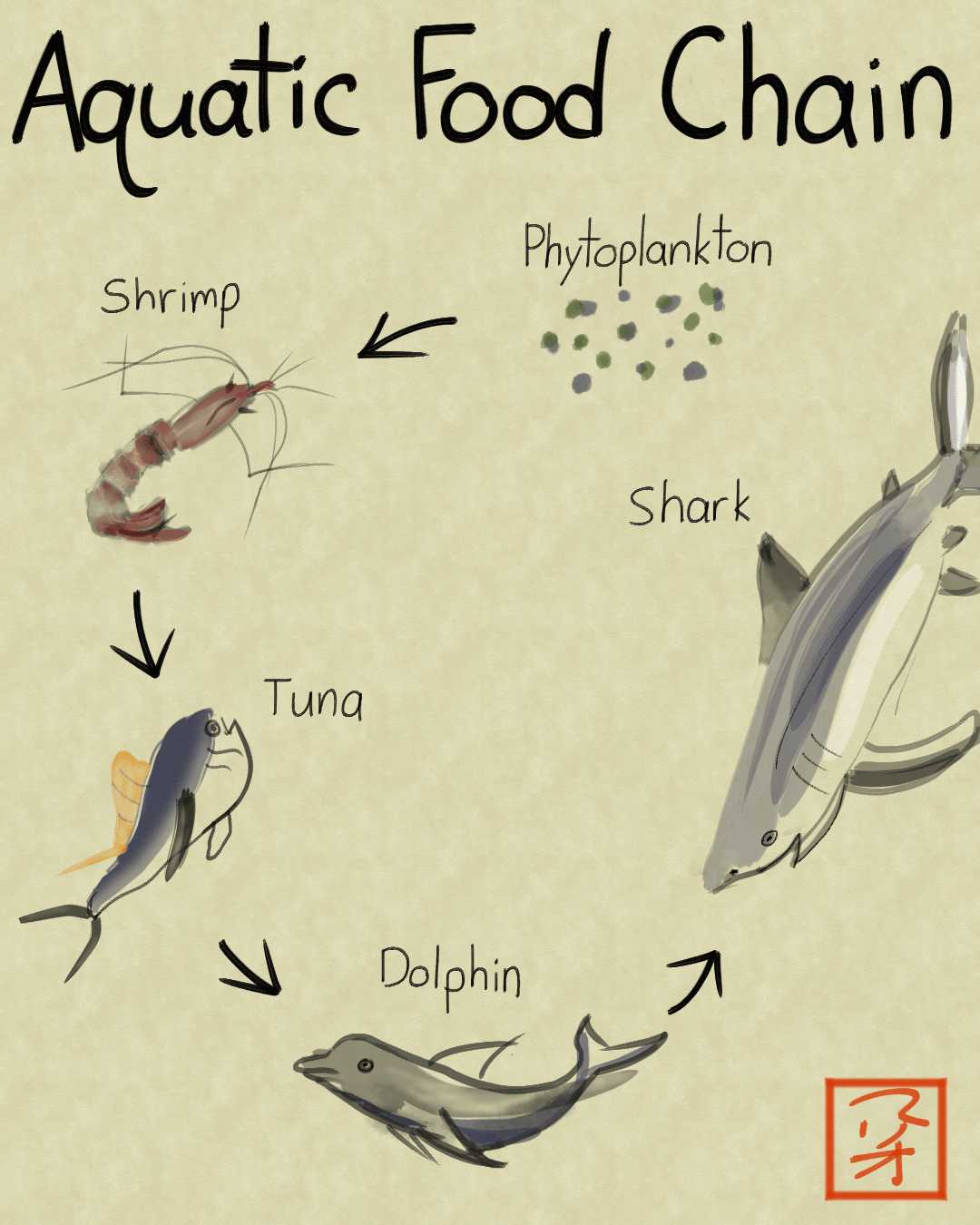
Primary consumers mostly herbivores exist at the next level and secondary and. Food chain is a chart showing the flow of energy food from one organism to the next beginning with a producer. A food chain outlines who eats whom.
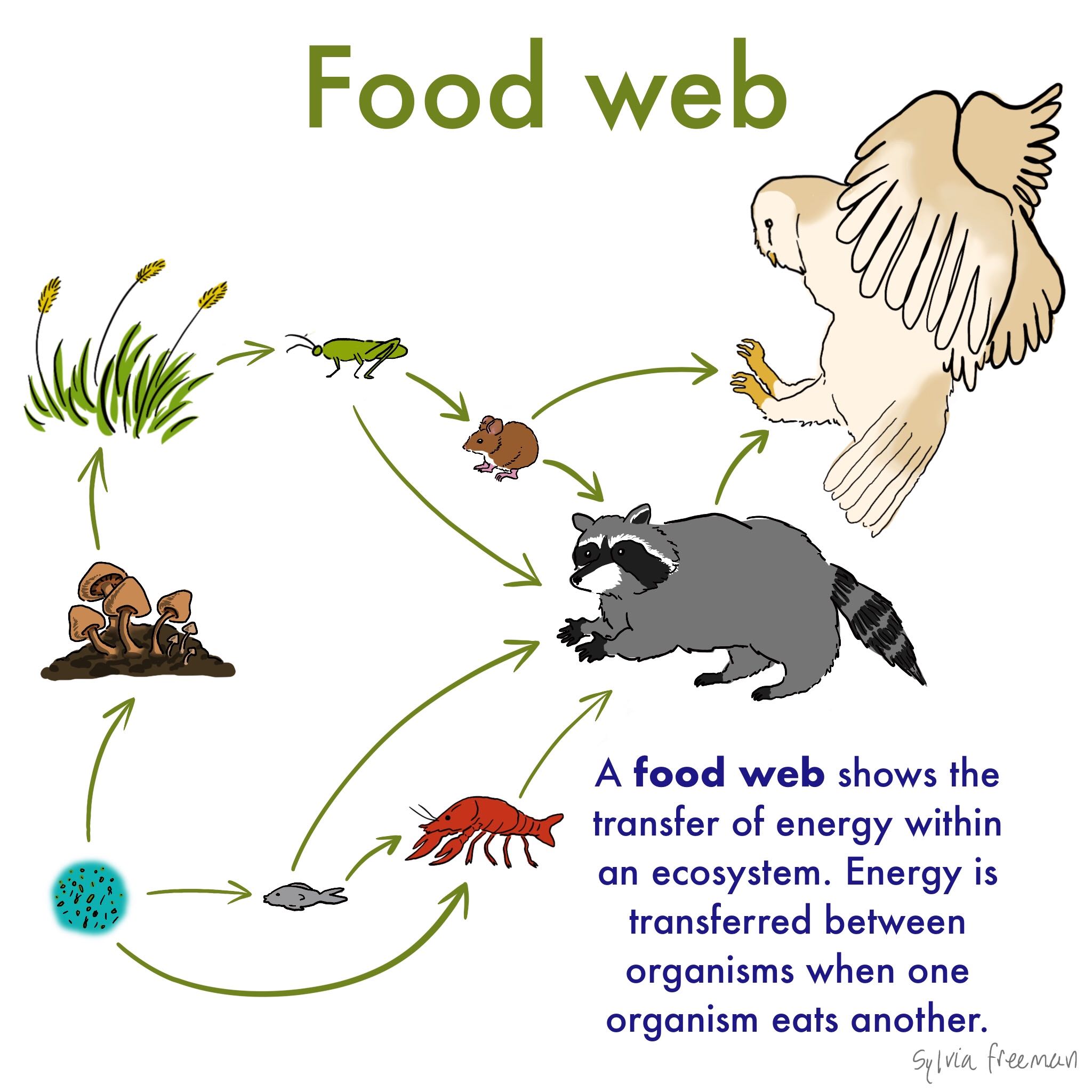
Shows what eats what in a particular habitat. In a community which has producers consumers and decomposers the energy flows in a specific pathway. That is they can form one of the links in a food chain.
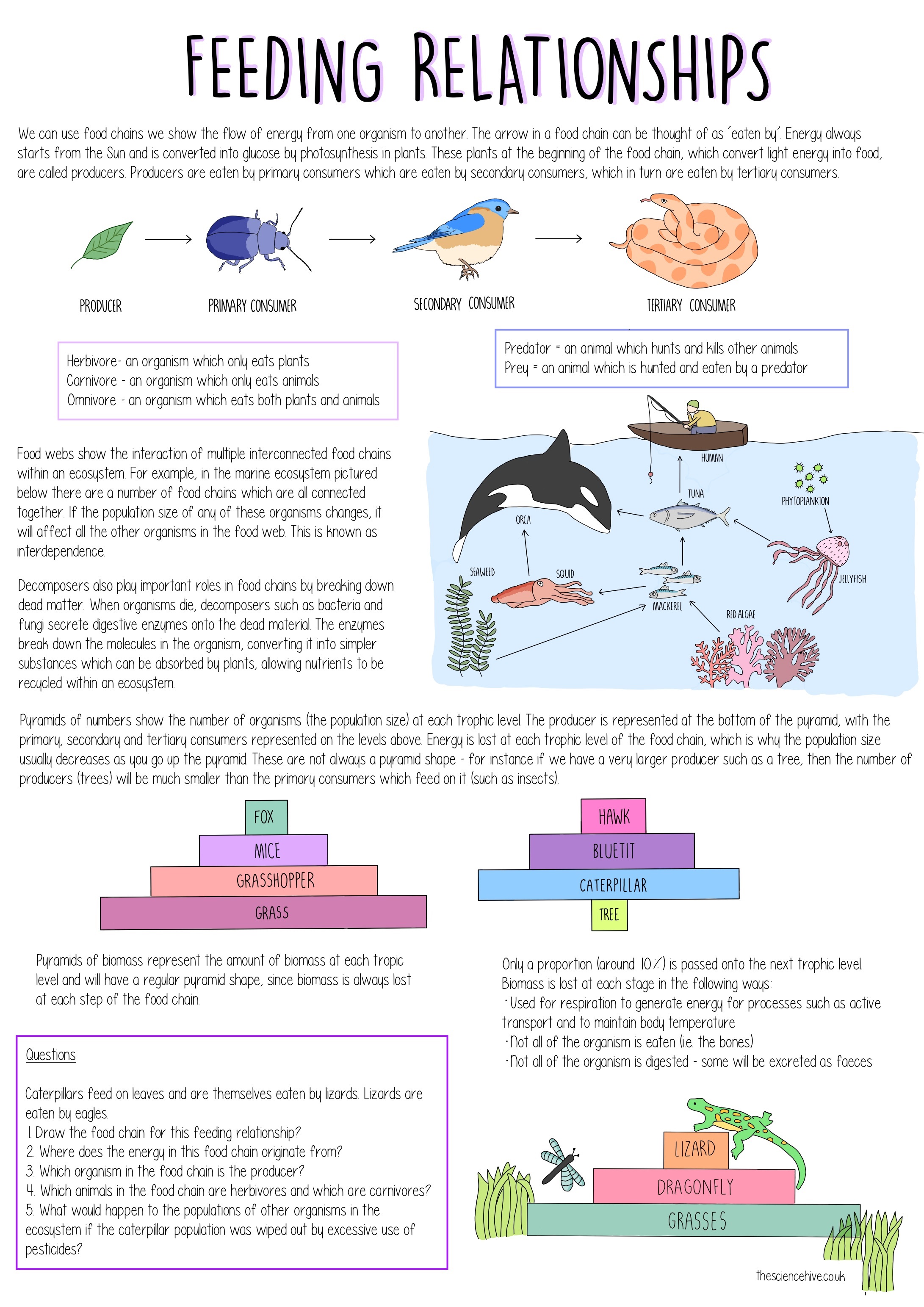
The food chain is a linear sequence of organisms where nutrients and energy is transferred from one organism to the other. Definition of food webs- Food chains are not strictly linear they have branches type link one food chain with another there may be several interlinked food chains in a community and one animal may be a link in more than one food chains the process of interlink a network of food chain in a community is called food webs food webs includes all the feeding relationships in ecosystem. The feeding level is known as the trophic level.
A food chain usually starts with a photosynthetic plant which gains its energy from the Sun. A sequence usually shown as a diagram of feeding relationships between organisms showing who eats what and the movement of energy through trophic levels. 5 hours ago A food chain is a series of interdependent relationships between living organisms.
An organism that obtains its energy by eating other organisms. Producers who make their own food using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis make up the bottom of the trophic pyramid. This occurs when one organism consumes another organism.