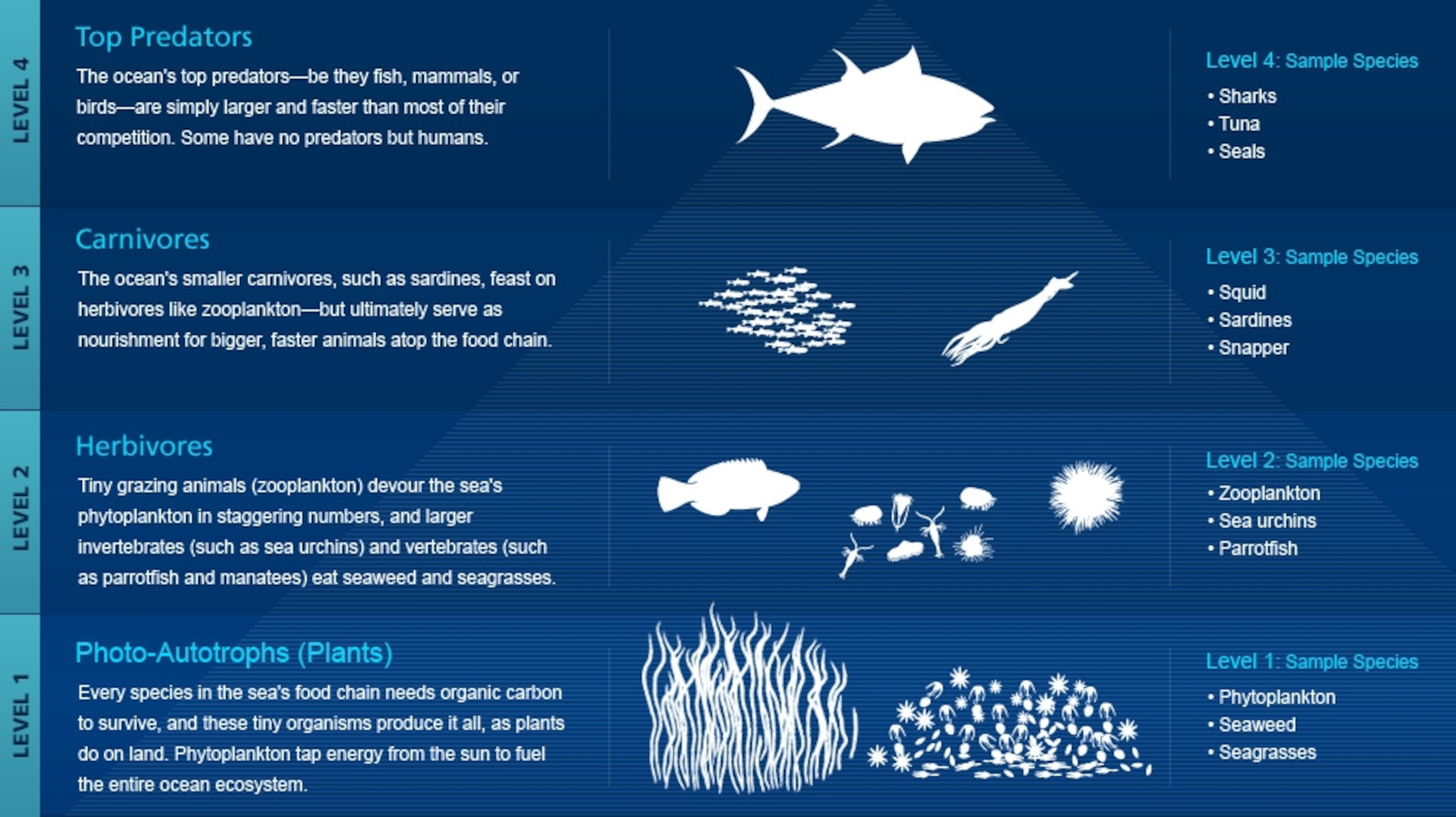
Marine Animals Definition Biology

Marine biology the science that deals with animals and plants that live in the sea.
Marine animals definition biology. Marine biologists study biological oceanography and the associated fields of chemical physical and geological oceanography to understand marine organisms. In this context the word marine is interchangeable with saltwater. Marine biology is the study of plants and animals that live in saltwater therefore a marine biologist is someone employed in that field of study.
Marine biology is the study of marine organisms their behaviors and interactions with the environment. Marine biology is the study of marine ecosystems marine organisms and human interactions with these environments and species. Marine biologists may have many different jobs including working with marine mammals eg a dolphin researcher studying the seafloor researching algae or even working with marine microbes in a lab.
It is the largest and most diverse biome in the world. Marine biology is the study of animals that live in the oceans or other marine water bodies. Most marine biologists choose a specialty field such as phycology ichthyology invertebrate zoology marine mammalogy fishery biology marine biotechnology marine microbiology or marine ecology.
Marine environments are therefore the most common habitat on Earth. Our ocean coasts and estuaries are home to diverse living things. So a marine biologist studies.
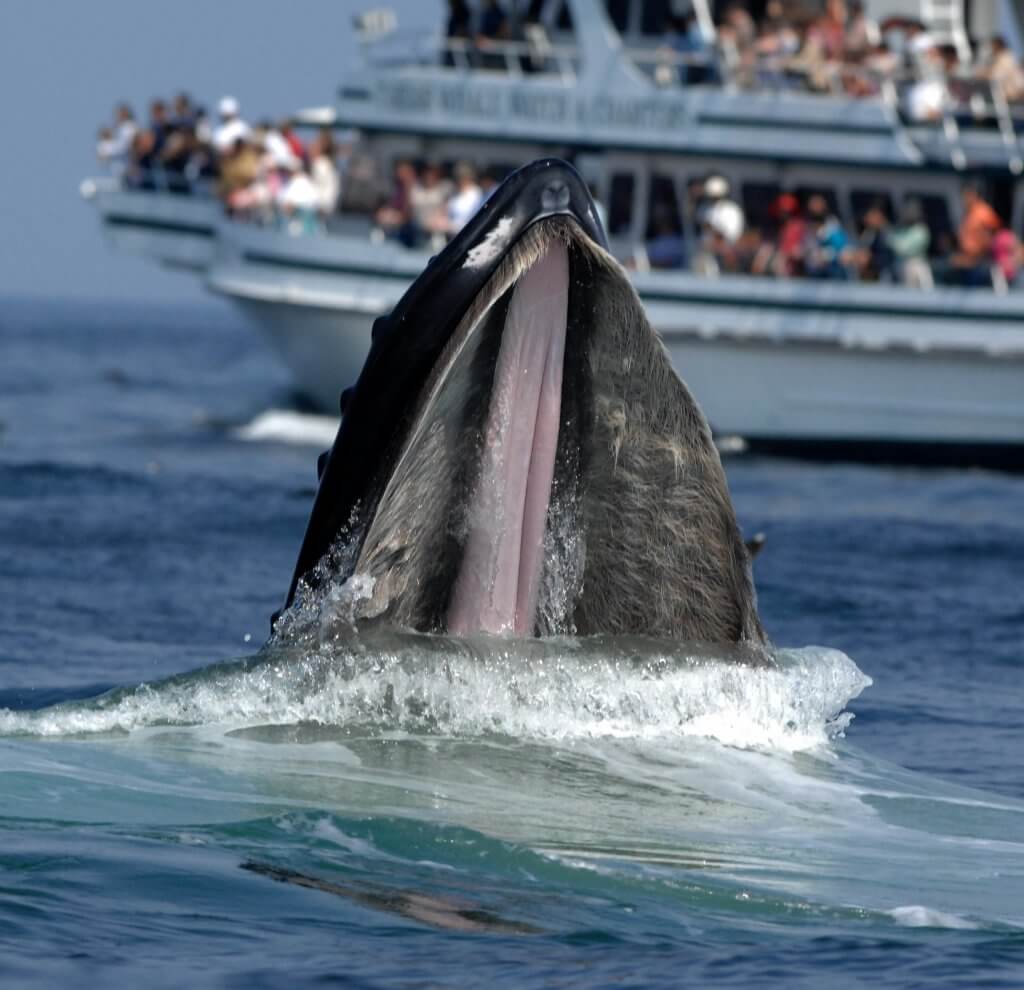
Marine life definition biology. Marine biology is the scientific study of plants and animals that live in salt water. An animal belonging to the mammalian order Sirenia which includes manatees and dugongs.
Not only that but water provides a 3-dimensional habitat which increases the available habitat for the animals microbes and plants to live. Given that in biology many phyla families and genera have some species that live in the sea and others that live on land marine biology classifies species based on the environment rather than on taxonomy. Spongin- flexible protein fibers.