Transgenic Animals Online Biology Notes

Transgenic animals 1.
Transgenic animals online biology notes. Example- Transgenic rats rabbits pigs sheep etc. June 4 2021 Gaurab Karki 0. Gardnerella vaginalis associated Bacterial Vaginosis BV.
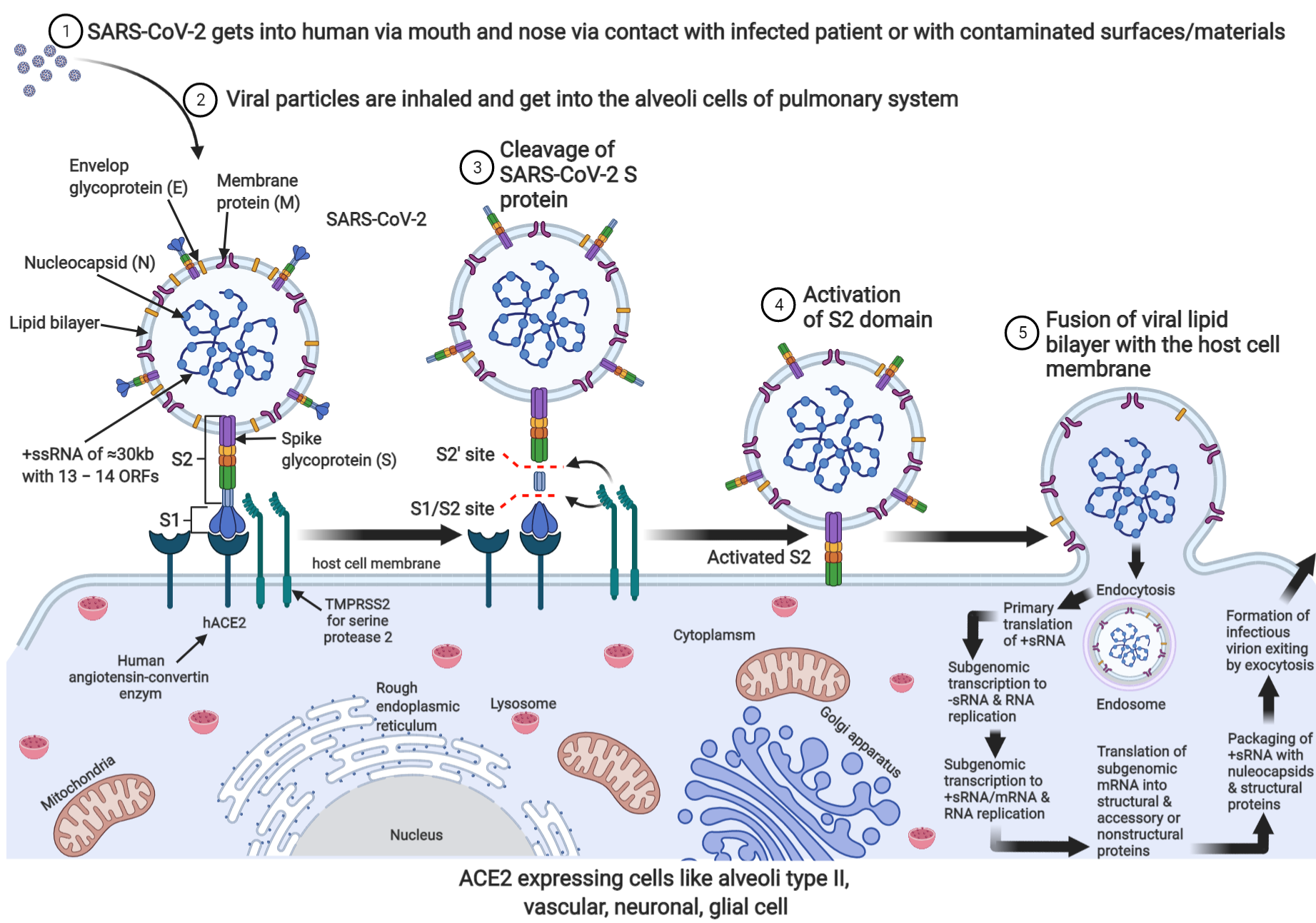
Vorticella Lvortexwhirl pool is a microscopic unicellular eukaryotic ciliate. After injecting the DNA the embryo is implanted into the uterus of receptive females. The dependence of man on animals such as cattle sheep poultry pig and fish for various purposes milk meat eggs wool etc is well known.
The first transgenic animal was produced in 1983 when genes for human growth hormone were introduced into mice. The most common method for producing transgenic plants is Agrobacterium-mediated transformation Figure PageIndex1Agrobacterium tumifaciens is a soil bacterium that as part of its natural pathogenesis injects its own tumor-inducing T i plasmid into cells of a host plantThe natural T i plasmid encodes growth-promoting genes that cause a gall ie. The foreign gene is constructed using recombinant DNA methodology.
In addition to the gene itself the DNA usually includes other sequences to enable it to be incorporated into the DNA of the host and to be expressed correctly by the cells of the host. Clinical cultural and Biochemical diagnosis. Transgenesis is the process by which mixing up of genes takes place.
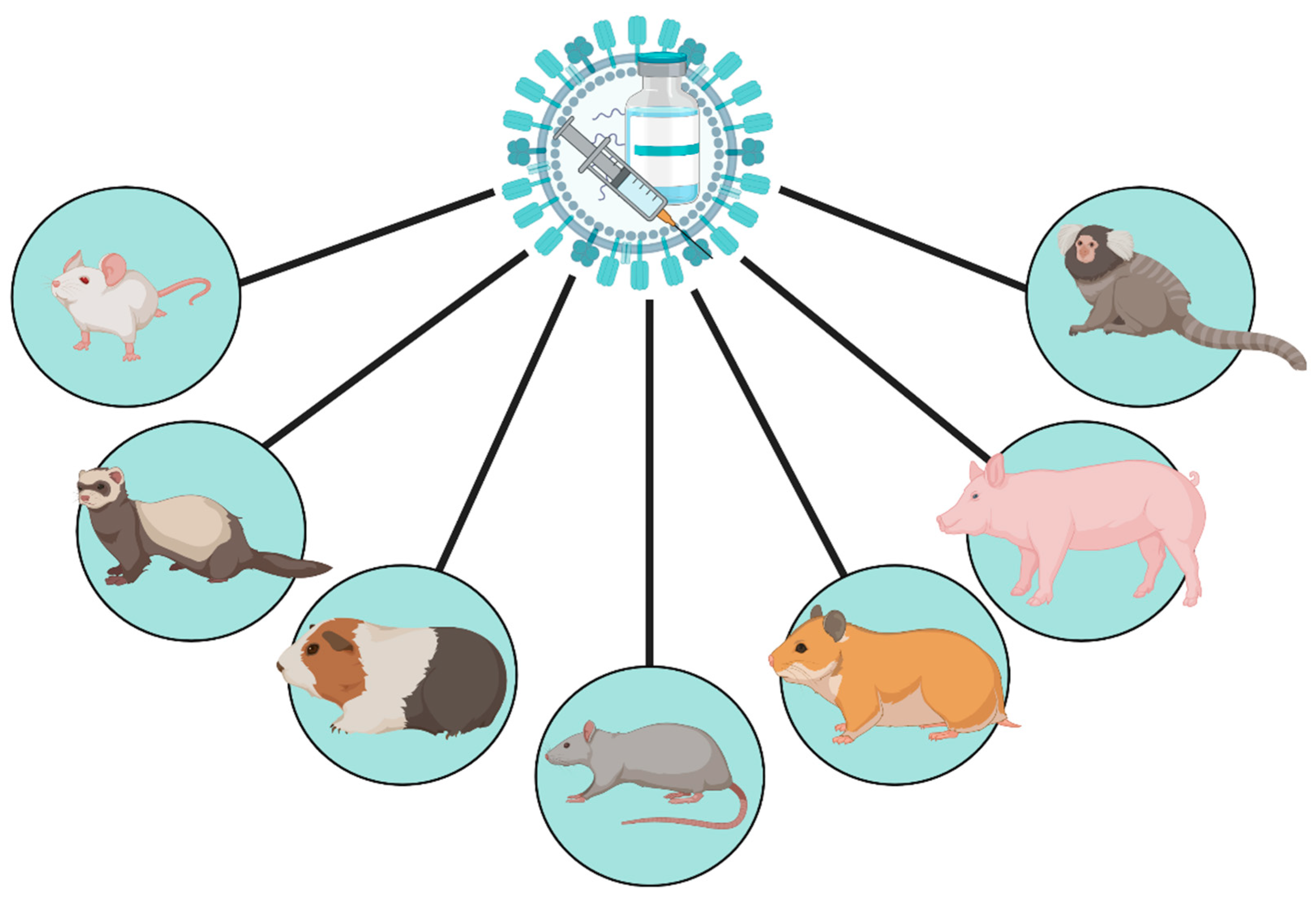
Improvement in the genetic characteristics of livestock and other domestic animals eg high milk yield weight gain etc in the early. Transgenic mice are developed by injecting DNA into the oocytes or 1-2 celled embryos taken from female mice. Transgenic rats rabbits pigs sheep cows and fish- Over 95 of the transgenic animals are miceBenefits of transgenic animals To study regulation of genes and their action on normal physiology development.
The Human Genome Project revealed that the human genome contains only 20000 to 25000 genes. Transgenic animals have great importance as 1 to study the normal physiology and development working of genes their regulation etc. One whose genome has been altered in a heritable manner by introduction of a foreign DNA sequence into genome of its zygote or embryo.